The Comparison of Several Rock Bolts for Slope Stability
Time:2025-03-23From:sinorock View:
Introduction
Slope stability is a critical concern in geotechnical engineering, especially in the construction of infrastructures like roads, railways, dams, and buildings on or near slopes. Stabilizing slopes to prevent landslides and other forms of soil and rock displacement is vital for ensuring the safety and longevity of these structures. One of the most effective methods for stabilizing slopes is the use of rock bolts. Currently, there are various types of rock bolts used for this purpose, including rebar anchor bolts, hollow bolts, and self-drilling rock bolts. Each type of rock bolt has its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, making them suitable for different slope conditions.
Rebar Anchor Bolt
What is a Rebar Anchor Bolt?
Rebar anchor bolts are among the most commonly used rock bolts for slope stabilization due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of production. A rebar anchor bolt is essentially a steel rebar with a standard thread on its surface, which allows it to be easily inserted into pre-drilled holes and secured with grout. The materials required for rebar anchor bolts are readily available, making them a popular choice for projects where budget constraints are a significant consideration.
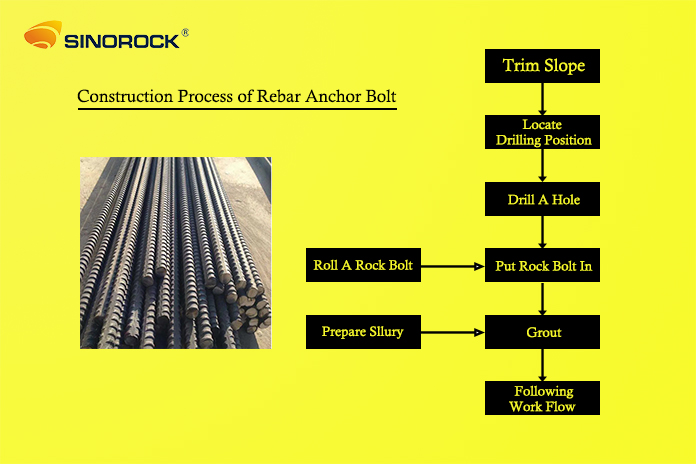
Construction Process
The construction process for installing rebar anchor bolts involves several steps to ensure the stability and safety of the slope. Here is a detailed breakdown of the process:
1. Trim Slope: The first step involves trimming the slope to remove any loose rocks and debris that could fall during the construction process. This step is crucial for creating a safe working environment and ensuring the effectiveness of the stabilization efforts.
2. Locate Drilling Position: Engineers must calculate the total load that the slope needs to bear to determine the number and placement of rebar anchor bolts. This step involves careful planning and precise calculations to ensure the bolts are correctly positioned to provide optimal support.
3. Drill a Hole: Using a drilling rig, a hole is drilled to the required depth. The diameter and depth of the hole depend on the design specifications and the geological conditions of the slope. A drill rod is used in this step to ensure the hole is straight and of the correct dimensions.
4. Insert Rock Bolt: Once the hole is drilled, the drill rod is removed, and the rebar anchor bolt is inserted into the hole. The bolt should be rolled in advance to facilitate its insertion and ensure a tight fit within the hole.
5. Grout: Finally, grout is injected into the hole using a grouting machine and a grouting pipe. The water-cement ratio of the grout typically ranges from 0.45 to 0.6:1. The grout fills the space around the bolt, securing it in place and providing additional strength to the slope.
When to Use a Rebar Anchor Bolt?
Rebar anchor bolts are best suited for stabilizing slopes with good geological conditions that allow for separate drilling and grouting processes. They are ideal for projects where cost savings are a priority, and the slope conditions are favorable for traditional drilling and grouting methods. However, their use may be limited in more challenging geological conditions where advanced techniques are required.
Hollow Bolt
What is a Hollow Bolt?
Hollow bolts represent a more advanced solution for slope stabilization compared to rebar anchor bolts. A hollow bolt serves dual functions: it acts as both a drilling rod and a grouting pipe. This dual functionality simplifies the construction process, reduces the construction time, and lowers the overall cost of the project. Hollow bolts are designed to be installed quickly and efficiently, making them a popular choice for projects with tight schedules.

How Does a Hollow Bolt Work?
The installation of a hollow bolt involves a streamlined process that combines drilling and grouting into a single step. Here is a detailed breakdown of how a hollow bolt works:
1. Drill a Hole: Similar to the rebar anchor bolt process, a drilling rig is used to drill a hole to the required depth. The hollow bolt itself acts as the drill rod, eliminating the need for a separate drilling rod.
2. Grout Injection: Once the hole is drilled, grout is injected through the hollow core of the bolt. This simultaneous drilling and grouting process ensures that the bolt is securely anchored within the hole and that the surrounding rock or soil is reinforced.
When to Use a Hollow Bolt?
Hollow bolts are suitable for reinforcing slopes with good geological conditions that allow for simultaneous drilling and grouting. They are particularly advantageous in projects where time and efficiency are critical factors. The reduced construction time and simplified process make hollow bolts an excellent choice for projects with tight deadlines or where minimizing disruption to the surrounding area is essential.
Self-Drilling Rock Bolt
What is a Self-Drilling Rock Bolt?
Self-drilling rock bolts represent the most advanced technology in slope stabilization. A self-drilling rock bolt system consists of several components, including a one-time-use drill bit, a hollow bar that can be cut or extended using couplers, a coupler, a plate, a nut, and a centralizer. This system is designed to provide maximum efficiency and effectiveness in stabilizing slopes, particularly in challenging geological conditions.
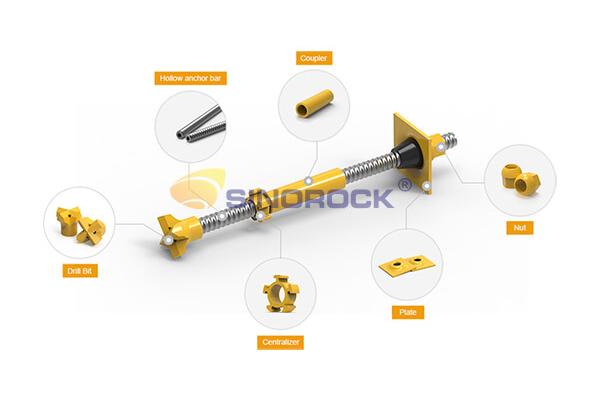

Construction Process
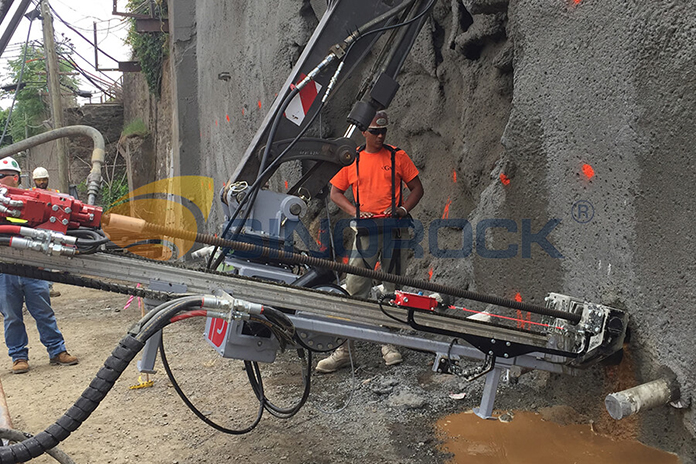
The construction process for installing self-drilling rock bolts is highly efficient, combining several steps into one seamless operation. Here is a detailed breakdown of the process:
1. Trim Slope: As with the other types of bolts, the first step involves trimming the slope to remove any loose rocks and debris. This step ensures a safe working environment and enhances the effectiveness of the stabilization efforts.
2. Locate Drilling Position: Engineers must calculate the total load and determine the optimal placement of the self-drilling rock bolts. This step involves precise calculations and careful planning to ensure the bolts provide maximum support.
3. Simultaneous Drilling and Grouting: The self-drilling rock bolt system allows for simultaneous drilling and grouting in one step. The hollow bolt body doubles as both a drill pipe and a grouting pipe, enabling the construction team to drill and inject grout simultaneously. This process significantly reduces the construction time and ensures a secure and stable installation.
How Does It Work?
During the drilling process, the self-drilling hollow bolt body serves multiple functions. It acts as a drill pipe, creating the hole, and as a medium transmission channel for the grout. After drilling into the rock formation, cement slurry is injected through the hollow core of the bolt to anchor it in place. The cement slurry fills any fissures in the rock, consolidating loose material and preventing the hole from collapsing. This process ensures a strong and stable anchoring effect, even in challenging geological conditions.
When to Use a Self-Drilling Rock Bolt?

Self-drilling rock bolts are ideal for stabilizing slopes in complex geological conditions where traditional drilling and grouting methods may not be effective. They are suitable for use in broken rock, loose soil, and other challenging environments. The self-drilling rock bolt system provides a safe, efficient, and convenient solution for slope stabilization in a variety of applications, including tunnel and underground engineering, slope engineering, and ground and foundation engineering. This system is particularly beneficial in projects where ensuring the anchoring effect in difficult ground conditions is critical to achieving the best construction results.
Comparison of Rock Bolts
Cost
One of the primary factors to consider when choosing a rock bolt for slope stabilization is cost. Rebar anchor bolts are generally the most economical option due to their simple design and readily available materials. Hollow bolts, while more expensive than rebar anchor bolts, offer cost savings through reduced construction time and labor. Self-drilling rock bolts are the most expensive option due to their advanced technology and specialized components. However, they can provide significant cost savings in projects with challenging geological conditions by reducing the need for additional support measures and minimizing construction time.
Construction Time
Construction time is another critical factor in selecting the appropriate rock bolt for slope stabilization. Rebar anchor bolts require separate drilling and grouting processes, which can extend the construction time. Hollow bolts streamline the process by combining drilling and grouting into a single step, reducing the overall construction time. Self-drilling rock bolts offer the most significant time savings by integrating drilling, grouting, and anchoring into one seamless operation. This efficiency makes them ideal for projects with tight deadlines or where minimizing disruption is essential.
Installation Complexity
The complexity of installation is an important consideration, particularly in projects with challenging access or limited working space. Rebar anchor bolts require a multi-step installation process, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming. Hollow bolts simplify the installation process by combining drilling and grouting, making them easier and faster to install. Self-drilling rock bolts offer the most streamlined installation process, with all steps integrated into one operation. This simplicity makes them an attractive option for projects where ease of installation is a priority.
Performance in Different Geological Conditions
The performance of rock bolts in different geological conditions is a crucial factor in determining their suitability for a particular project. Rebar anchor bolts are best suited for stable geological conditions where traditional drilling and grouting methods are effective. Hollow bolts provide better performance in moderately challenging conditions by simplifying the installation process and reducing the risk of hole collapse. Self-drilling rock bolts offer the best performance in complex geological conditions, including broken rock and loose soil, where traditional methods may not be effective. Their ability to drill, grout, and anchor simultaneously ensures a secure and stable installation in even the most challenging environments.
Long-Term Stability
Long-term stability is a key consideration in slope stabilization projects, as the effectiveness of the rock bolts must be maintained over time. Rebar anchor bolts provide reliable long-term stability in suitable geological conditions but may be less effective in challenging environments. Hollow bolts offer improved long-term stability by reducing the risk of hole collapse and ensuring a secure anchoring effect. Self-drilling rock bolts provide the
highest level of long-term stability, particularly in complex geological conditions. Their advanced design and installation process ensure a strong and durable anchoring effect that can withstand the test of time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice of rock bolts for slope stabilization depends on various factors, including cost, construction time, installation complexity, performance in different geological conditions, and long-term stability. Rebar anchor bolts are an economical and widely used option for projects with stable geological conditions and budget constraints. Hollow bolts offer a more advanced solution with reduced construction time and improved performance in moderately challenging conditions. Self-drilling rock bolts represent the most advanced technology, providing the best performance and long-term stability in complex geological conditions.
Each type of rock bolt has its unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications and project requirements. By carefully considering these factors and selecting the most appropriate rock bolt for the specific conditions of the slope, engineers can ensure the safety, stability, and longevity of their projects.
latest news
-

- The Comparison of Several Rock Bolts for Slope Stability
- Time:2025-03-23From:This Site
- There are various types of rock bolts used for this purpose, including rebar anchor bolts, hollow bolts, and self-drilling rock bolts. Each type of rock bolt has its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, making them suitable for different slope conditions.
- View details
-

- Types of Self-Drilling Rock Bolt Drill Bits and Applicable Geological Conditions
- Time:2025-03-14From:This Site
- The drill bit is an important part of the self-drilling rock bolt, and it is a necessary condition for the integration of the three functions of drilling, grouting, and anchoring.
- View details
-

- Four Common Methods for Slope Support
- Time:2025-03-12From:This Site
- Slope stability is a critical factor in various construction and engineering projects. When dealing with steep slopes or excavations, it is essential to implement effective slope support methods to ensure safety and prevent potential disasters such as landslides or slope failures. There are a variety of common slope support methods that need to be selected based on the soil conditions and support needs of the construction site. In this article, we will explore four common methods for slope support.
- View details
-

- Quality Control: the Vital Factor of A SDA Bolt Factory
- Time:2025-01-09From:This Site
- Sinorock’s comprehensive quality control system, from supplier management to outgoing inspections, ensuring the highest standards for self-drilling anchor bolts in construction.
- View details
-
.png)
- International Women's Day with Strawberry-picking
- Time:2024-03-09From:This Site
- Marked the annual observance of International Women's Day, and to commemorate this significant event, Sinorock organized a special strawberry-picking event exclusively for its female employees.
- View details
-

- Celebrate the 74th anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China
- Time:2023-10-01From:This Site
- On October 1st every year, we observe the annual National Day, commemorating the birth of our beloved motherland.
- View details
-

- Sinorock Invites You to Explore Proven Self-Drilling Anchor Bolt Solutions at bauma 2025
- Time:2025-03-07From:This Site
- From April 7–13, 2025, explore Sinorock’s Self-drilling anchor bolt solution at Booth C2.513/4 in Hall C2 of the Messe München Exhibition Center (Munich, Germany).
- View details
-
.jpg)
- SINOROCK to Attend EXPOMINA PERÚ 2024 in Lima, Peru
- Time:2024-08-10From:This Site
- Sinorock to Attend EXPOMINA PERÚ 2024 in Lima, Peru
- View details
-
.jpg)
- SINOROCK to Participate in MINING AND METALS CENTRAL ASIA 2024
- Time:2024-08-08From:This Site
- SINOROCK to Participate in MINING AND METALS CENTRAL ASIA 2024
- View details
 Download
Download 


